Saurabh Kalra
- August 25, 2024
- No Responses

Excerpt :
In a world constrained by finite resources, the circular economy isn't just a way forward; it's the only way forward. It's about ending the cycle of waste, not just managing it.
The concept of the circular economy (CE) has emerged as a transformative model aimed at addressing the pressing environmental challenges posed by the traditional linear economy. The linear model, characterized by a ‘take-make-dispose’ approach, has led to significant resource depletion, waste generation, and environmental degradation. In contrast, the circular economy seeks to redefine growth by emphasizing the sustainable use of resources, waste minimization, and the regeneration of natural systems. This article delves into the principles of the circular economy and highlights innovative solutions for waste reduction and recycling.
Principles of the Circular Economy
The circular economy is underpinned by three core principles: eliminating waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. These principles serve as the foundation for transforming our traditional linear economy into a circular one that is restorative and regenerative by design.
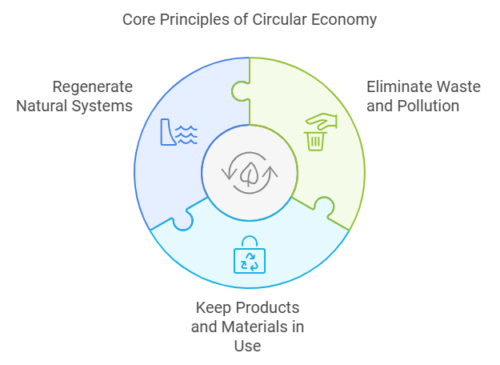
Innovative Solutions for Waste Reduction
Innovative technologies and practices are at the forefront of waste reduction efforts within the circular economy. These solutions range from advanced recycling technologies to smart waste management systems that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
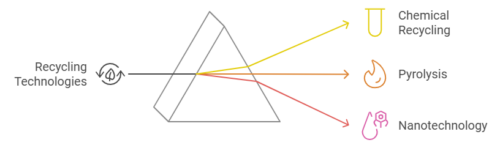
Advanced Recycling Technologies
Recycling is a critical component of the circular economy, and recent advancements in recycling technologies are revolutionizing waste management. These innovations include chemical recycling, pyrolysis, and nanotechnology.
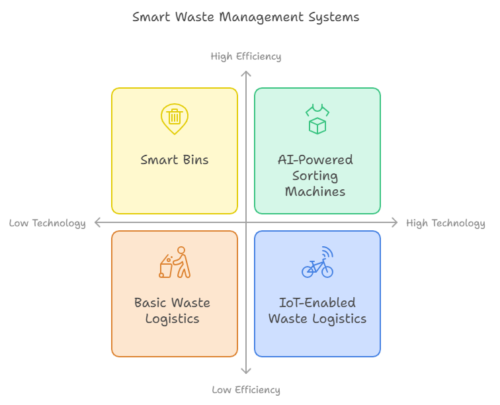
Smart Waste Management Systems
Smart waste management systems utilize AI and IoT to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of waste collection, sorting, and recycling processes. These systems include smart bins, AI-powered sorting machines, and IoT-enabled waste logistics.

Case Studies of Circular Economy Innovations
Several companies and organizations are leading the way in implementing circular economy principles and innovative waste reduction solutions. These case studies highlight the practical applications and benefits of the circular economy.
RiverRidge
RiverRidge is a waste management company in Northern Ireland that specializes in recycling and material recovery. The company leverages advanced technologies to optimize waste collection, improve recycling processes, and enhance overall efficiency. By utilizing cutting-edge tools and systems, RiverRidge is able to streamline operations, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. For example, the company uses AI and IoT to monitor waste levels in real-time, enabling more efficient waste collection and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste Solutions
Waste Solutions is a waste management company that utilizes smart waste technology to provide customized waste disposal and recycling programs. The company offers tailor-made solutions for managing and recycling food waste, as well as safely disposing of bio-medical waste and bio-hazardous materials. By incorporating AI and ultra-sonic technology, Waste Solutions can optimize efficiency and improve service transparency, helping clients achieve waste reduction and diversion goals.
PureCycle Technologies
PureCycle Technologies has developed a process to recycle contaminated plastic waste into high-quality, reusable resin. This technology removes contaminants, color, and odor from plastics, leaving behind a pure resin that can be used to create new products. By addressing the challenges of plastic waste contamination, PureCycle is contributing to the circular economy by enabling the recycling of previously non-recyclable plastics.
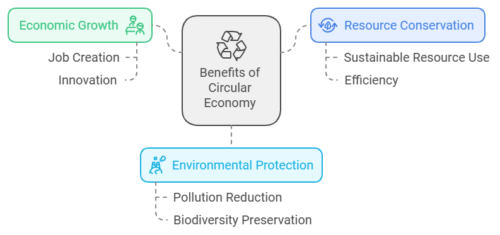
Benefits of the Circular Economy
The shift to a circular economy offers numerous benefits for businesses, society, and the environment. These benefits include economic growth, resource conservation, and environmental protection.
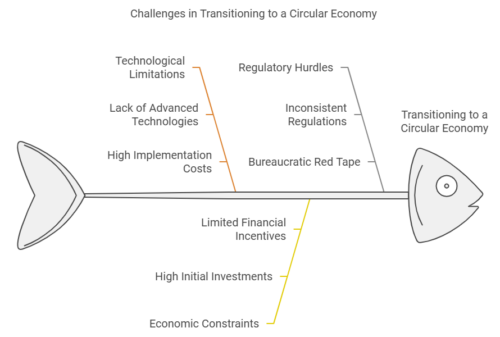
Challenges and Barriers to the Circular Economy
Despite its numerous benefits, the transition to a circular economy faces several challenges and barriers. These include technological limitations, economic constraints, and regulatory hurdles.
Conclusion
The rise of the circular economy represents a paradigm shift in how we approach production, consumption, and waste management. By embracing the principles of eliminating waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems, the circular economy offers a sustainable alternative to the traditional linear economy. Innovative solutions for waste reduction and recycling, such as advanced recycling technologies and smart waste management systems, are driving the transition to a circular economy. Despite the challenges and barriers, the circular economy holds the promise of economic growth, resource conservation, and environmental protection. As businesses, policymakers, and individuals continue to adopt circular economy practices, we can move towards a more sustainable and resilient future.

Meet Saurabh Kalra, a passionate Sustainability coach, an entrepreneur, storyteller, and the creative force behind "Green biz talks." He is a Doctorate Scholar at SSBM Geneva and an Engineering Graduate with an MBA degree. His expertise in the subject and over 20 years of industry experience clubbed with an insatiable curiosity and an unquenchable thirst for new experiences, makes him one of the most sought-after sustainability compliance experts in India. Reach out to him for speeding up your sustainable certification journey.
We Help you get Green Certifications for your Business ! Call us Now

Leave a Comment